Renewable Resources
Renewable raw materials are agricultural and forestry products which are not used for food or feed, but instead used for materials or to produce heat, electricity or fuel.
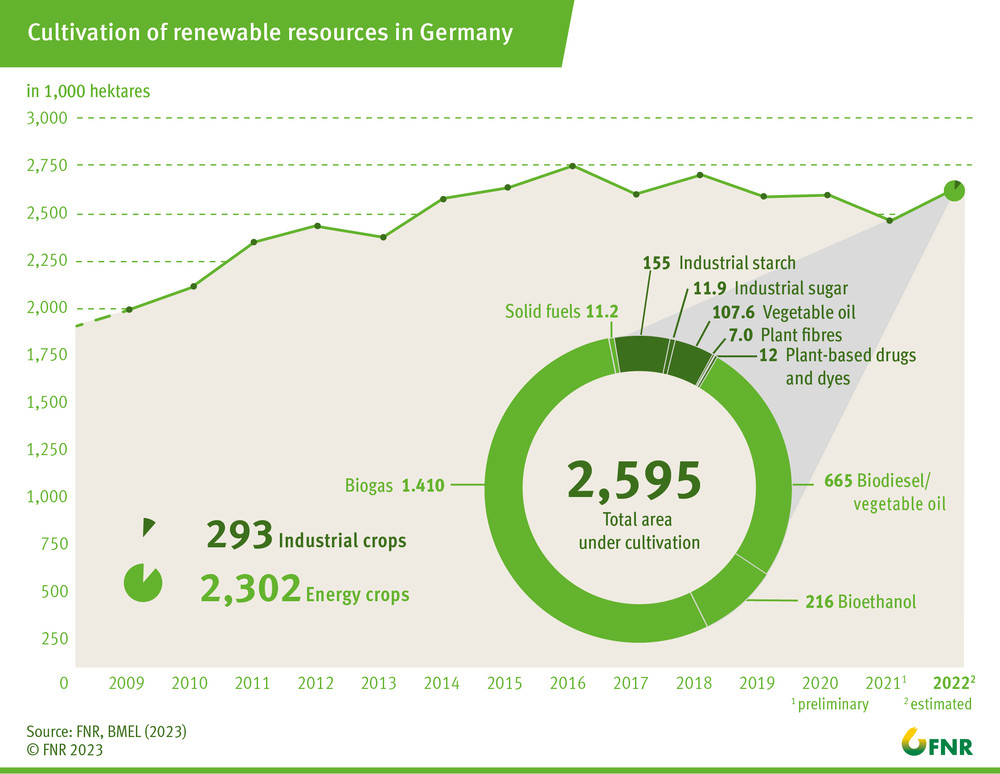
In Germany, renewable raw materials were grown on nearly 2.63 million hectares in 2021, thereof energy crops on 2.24 million hectares. That is about 14% of the arable land. In addition the forest area in Germany takes about 11 million hectares – which is at least one-third of Germany´s total area and also provides a huge amount of renewable raw materials (Bioenergy in Germany: Facts and Figures 2020). The average annual timber harvesting amounted to ca. 68 million m3 in 2019 (BMEL, DESTATIS), of which half was put to material use (construction and housing, cellulose production and other), and the rest to energetic use (households, heating and co-generation plants).
Renewable raw materials help to curb climate change, by releasing less greenhouse gas than fossil raw materials when used for energetic purposes and even binding carbon dioxide when used for material purposes. They serve the security of supply, because they are not finite and can be found in almost all countries of the world. Their use is often associated with environmental benefits, for example in environmentally sensitive areas. The manufacturing of products made from renewable resources is often less (eco-)toxic and moreover less energy-intensive. In addition, the cultivation of renewable raw materials, contrary to public perception, doesn’t only pose risks but also offers opportunities for a wider range of species in agriculture landscape. After all, the range of energy- and raw material plants is wide and much greater than the range of food and fodder crops grown today.
When renewable raw materials from domestic agriculture and forestry are produced and processed in Germany and further consumed here, the added value stays in the country and usually new jobs are generated. Especially in rural areas that are underdeveloped and affected by brain drain, this offers great opportunities and new perspectives for the local population.
Renewable raw materials are used in diverse areas of the industry and private sector. Besides storable bioenergy, which can be converted into electricity, heat and/or fuel in various processes, there is an immense range of products made of renewable raw materials. It ranges from building materials to paper and cardboard, construction materials, lubricants, intermediate and finished products for the chemical industry, medicines, cosmetics, dyes, textiles, and much more.